Cold Plasma Market Size and Forecast 2025 to 2034
The global cold plasma market size was valued at USD 258.35 million in 2024 and is anticipated to reach around USD 1,129.91 million by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 15.9% from 2025 to 2034. Increased adoption of cold plasma in advanced manufacturing processes, growing awareness of various benefits, rising demand for semiconductors and surging healthcare expenditure are driving the growth of the cold plasma market.
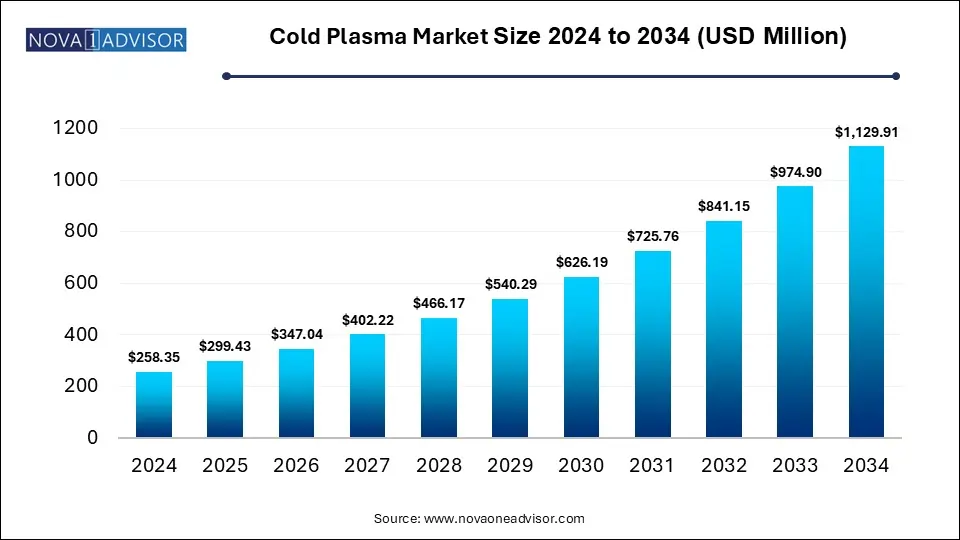
Cold Plasma Market Key Takeaways
- The atomic pressure product segment led the market and accounted for the largest revenue share of 66% in 2024.
- Low-pressure segments are expected to grow at a CAGR of 15.6% over the projected years.
- The wound healing application segment dominated the market and accounted for the largest revenue share of 32% in 2024.
- The cancer treatment applications segment is expected to grow at a CAGR of 17% over the forecast years.
- The North America cold plasma market dominated the global market and accounted for the largest revenue share of 42% in 2024.
- The cold plasma market in Asia Pacific is expected to grow at a CAGR of 16.8% over the forecast years.
Market Overview
The cold plasma market is evolving as a transformative space in the intersection of medicine, biotechnology, and materials science. Also known as non-thermal plasma, cold plasma is an ionized gas consisting of ions, electrons, and neutral particles that remain at near-room temperature, making it safe and effective for use in a range of biological and medical applications. Unlike traditional plasmas, which operate at high temperatures, cold plasma can be generated under low or atmospheric pressure conditions without damaging living tissues, thus making it particularly suitable for healthcare innovations.
Recent years have seen a surge in interest around cold plasma technology, especially in the medical field. This surge is driven by its non-invasive nature, antimicrobial efficacy, and potential to accelerate tissue regeneration and hemostasis. In the healthcare industry, cold plasma is gaining traction for its use in wound healing, cancer therapy, dental care, and even dermatological applications. Additionally, cold plasma’s role in sterilization and infection control aligns well with rising concerns about antibiotic resistance and hospital-acquired infections (HAIs), which are pressing global healthcare issues.
The market is also supported by increasing R&D funding, collaborations between research institutions and medical device companies, and growing awareness of its clinical benefits. Regulatory bodies such as the U.S. FDA and European CE mark authorities are gradually recognizing cold plasma-based technologies, with several companies receiving approvals for commercial deployment in therapeutic settings. Moreover, ongoing trials and pilot studies continue to expand the scope of cold plasma in emerging areas like oncology, neurological therapy, and vascular medicine.
In parallel, the non-medical applications of cold plasma — in areas like textile treatment, food safety, and environmental purification — further underscore its versatile value proposition. However, for this report, the focus remains on the medical applications that are shaping the future of healthcare and driving significant market growth across regions.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Surging Interest in Antimicrobial and Sterilization Applications: Cold plasma’s ability to deactivate bacteria, viruses, and fungi is fueling its adoption in infection control and medical sterilization.
-
Wound Care Advancements: Cold plasma devices are gaining clinical acceptance for accelerating chronic wound healing in diabetic patients and burn victims.
-
Growing Integration in Dental Clinics: Dentists are increasingly using cold plasma for cavity disinfection, biofilm removal, and gingival healing due to its non-invasive and painless nature.
-
Emergence of Cold Plasma Oncology Therapy: Clinical research is progressing in using cold plasma for targeting cancer cells without damaging surrounding tissues, creating hope for non-toxic adjunct cancer therapies.
-
Portable and Handheld Device Innovations: Manufacturers are developing lightweight, battery-operated cold plasma tools for use in ambulatory and home care settings.
-
Collaborative Research Ecosystem: Strategic partnerships between hospitals, research institutions, and med-tech companies are advancing the technology's clinical pipeline.
-
FDA and CE Approvals Gaining Momentum: Regulatory acceptance is growing, enabling wider commercial adoption and insurance coverage for plasma-based treatments.
-
High Demand for Non-Thermal Alternatives in Dermatology: Cosmetic and dermatology sectors are showing interest in cold plasma for skin rejuvenation, acne treatment, and scar reduction.
How is AI Influencing the Cold Plasma Market?
Artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms can be applied to analyze large amounts of data for optimizing plasma parameters in real-time offering enhanced precision and control, further leading to improved accuracy and efficacy of treatments. Automation of cold plasma generation and other applications with AI-powered systems can potentially increase the efficiency and mitigate human errors. AI can assist in prediction of potential issues related with cold plasma equipment, further allowing proactive maintenance and reduced downtimes in processes.
Cold Plasma Market Report Scope
| Report Attribute |
Details |
| Market Size in 2025 |
USD 299.43 Million |
| Market Size by 2034 |
USD 1,129.91 Million |
| Growth Rate From 2025 to 2034 |
CAGR of 15.9% |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025 to 2034 |
| Segments Covered |
Pressure, Application, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Report Coverage |
Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Bovie Medical Corporation.; Neoplas med GmbH; Europlasma NV; P2i Ltd.; US Medical Innovations; Apyx Medical.; Adtec Healthcare Limited.; terraplasma medical GmbH; CINOGY System GmbH |
Key Market Driver: Rising Prevalence of Chronic and Non-Healing Wounds
One of the strongest drivers for the cold plasma market is the rising burden of chronic and non-healing wounds worldwide. Diabetic ulcers, pressure sores, and post-surgical wounds that fail to heal within a standard timeline pose significant healthcare challenges, often leading to infections, amputations, and extended hospital stays. In the U.S. alone, it is estimated that over 6.5 million people suffer from chronic wounds, incurring billions of dollars in healthcare costs annually.
Cold plasma therapy offers a revolutionary solution by stimulating cell proliferation, increasing microcirculation, and exhibiting potent antimicrobial properties — all without damaging surrounding healthy tissue. These features make it particularly effective in diabetic foot ulcers, venous leg ulcers, and burn wounds. Several studies have demonstrated that cold plasma accelerates re-epithelialization and reduces bacterial biofilm load, leading to faster wound closure and reduced need for antibiotics. As healthcare systems globally focus on value-based care and cost-effective treatment modalities, the demand for innovative, non-invasive wound healing technologies like cold plasma is expected to soar.
Key Market Restraint: Limited Clinical Evidence and Regulatory Barriers
While cold plasma technology holds substantial promise, its widespread adoption in medical settings is restrained by limited clinical validation and regulatory complexities. Despite numerous pilot studies and preliminary trials, large-scale, randomized clinical trials demonstrating long-term efficacy and safety are still relatively scarce. As a result, clinicians and regulatory bodies often approach the technology with caution, leading to slower approval timelines and reimbursement hesitancy.
Additionally, the mechanism of action of cold plasma in biological systems is not yet fully understood, which complicates its standardization across various therapeutic applications. This knowledge gap creates challenges in creating uniform treatment protocols and hinders its integration into conventional medical practices. Medical device developers must also navigate complex regulatory environments that vary significantly by region, further delaying commercialization efforts. Until more robust clinical datasets and clear regulatory frameworks are established, the market may experience sporadic growth across certain applications.
Key Market Opportunity: Cold Plasma in Cancer Treatment
Cold plasma’s application in cancer treatment represents one of the most promising opportunities for future market expansion. Preliminary studies suggest that cold atmospheric plasma (CAP) can selectively target and kill cancer cells through oxidative stress mechanisms without harming healthy cells. This opens up potential avenues for non-invasive adjunct therapies in oncology, especially in cases where traditional chemotherapy and radiotherapy pose high toxicity risks.
Research has already shown encouraging results in cancers such as glioblastoma, melanoma, and pancreatic cancer. CAP induces apoptosis and DNA damage in malignant cells, reduces angiogenesis, and can potentially be used to enhance drug delivery by increasing cellular permeability. Moreover, cold plasma can be used intraoperatively to sterilize surgical margins and prevent tumor recurrence, making it a valuable tool during tumor excision procedures. With clinical trials gaining momentum in Europe, the U.S., and Asia-Pacific, this segment could evolve into a major revenue stream for manufacturers and significantly improve patient outcomes in cancer care.
Cold Plasma Market Report Segmentation Insights
By Pressure Insights
The atomic pressure product segment led the market and accounted for the largest revenue share of 65.32% in 2023. due to its ease of application and growing use in clinical settings. Atmospheric pressure cold plasma (APCP) devices are particularly well-suited for outpatient and bedside use because they do not require vacuum chambers or controlled environments. Their operational simplicity, portability, and ability to treat open wounds or skin surfaces without direct contact have made them ideal for dermatology clinics, dental practices, and emergency wound care units. These devices are also more scalable and cost-effective, contributing to their broad adoption across both developed and emerging economies.
Low-pressure segments are expected to grow at a CAGR of 15.6% over the projected years. This form of plasma is generated in vacuum chambers and allows for more precise control of plasma composition, energy, and exposure duration. It is particularly useful in applications that require uniform plasma treatment, such as sterilization of surgical instruments, pre-treatment of implants, or targeting internal tissue structures in experimental cancer therapies. While these systems are more complex and expensive, their potential for delivering high-intensity, focused therapeutic interventions is attracting growing attention in specialized hospital settings and research institutions.
By Application Insights
The wound healing application segment dominated the market and accounted for the largest revenue share of 31.45% in 2023. Supported by the growing prevalence of chronic wounds and increased investment in wound care technologies. Hospitals and outpatient centers are increasingly integrating cold plasma devices into their standard wound management protocols due to their non-contact, painless, and rapid action on infected and inflamed wounds. Studies have shown up to 60% faster wound healing in patients treated with cold plasma, compared to conventional dressings and antibiotics. With pressure ulcers and diabetic foot ulcers becoming more common among aging populations, this segment is poised for sustained growth.
The cancer treatment applications segment is expected to grow at a CAGR of 17% over the forecast years. Reflecting the technology’s early success in targeting malignant cells with minimal side effects. Research labs and oncology centers are beginning to deploy cold plasma for experimental cancer therapies, particularly in hard-to-treat solid tumors. Intraoperative use of plasma jets to sterilize surgical margins and target residual cancer cells is gaining traction as a promising adjunct therapy. As clinical validation progresses and oncologists become more familiar with its mechanism, this segment is expected to experience exponential growth over the next decade.
By Regional Insights
North America holds the largest market share in the global cold plasma market, primarily due to advanced healthcare infrastructure, strong R&D investment, and the presence of leading market players. The U.S. accounts for the lion’s share of regional revenue, driven by increasing clinical trials, early adoption by hospitals, and significant funding from institutions like the National Institutes of Health (NIH). Regulatory frameworks such as the FDA’s Breakthrough Devices Program have also supported faster commercialization of innovative plasma-based therapies. Furthermore, collaborations between academic institutions (like Harvard and Stanford) and med-tech firms continue to enhance product pipelines and market accessibility.
Asia-Pacific is the Fastest-Growing Region
Asia-Pacific is experiencing the fastest growth, fueled by rising healthcare expenditure, growing awareness of advanced wound care technologies, and increasing cancer prevalence. Countries such as China, India, and South Korea are investing in healthcare modernization and fostering public-private partnerships to bring cutting-edge therapies to market. Local manufacturers are also emerging with cost-effective, portable cold plasma devices, making the technology more accessible in rural and semi-urban healthcare settings. Additionally, Japan’s aging population and government-backed initiatives in medical innovation are fostering increased adoption of cold plasma in wound management and dermatological applications.
How is China Contributing to the Cold Plasma Market in Asia Pacific?
China is the leading contributor to the cold plasma market in the Asia Pacific. Rising applications of cold plasma technology in various such as in healthcare for wound healing and cancer treatment, in electronics for semiconductor manufacturing and surface modification as well as in environmental protection for water treatment and pollution control are driving the market growth. Advancements in material science are facilitating the development of more affordable and efficient cold plasma equipment. Furthermore, concerns regarding food safety, increased emphasis on sustainable solutions, rising healthcare expenditure and supportive government initiatives are driving the adoption of cold plasma technology in China.
Cold Plasma Market Top Key Companies:
- Bovie Medical Corporation
- Neoplas Med GmbH
- Europlasma NV
- P2i Ltd.
- US Medical Innovations;
- Apyx Medical.
- Adtec Healthcare Limited.
- terraplasma medical GmbH
- CINOGY System GmbH
Cold Plasma Market Recent Developments
- In June 2025, the breakthrough Neoplas Argon Jet system which utilizes cold atmospheric argon plasma for accelerated wound healing, stimulating tissue regeneration and to inactivate pathogens without any pain or side effects was launched in Oman. The new system developed through German-European scientific alliance that was led by Neoplas Med GmbH and the Leibniz Institute for Plasma Science and Technology complies with the EU Medical Device Regulation (MDR) standards and has a CE mark.
- In May 2025, PHLAS skincare technology, the first at-home skincare device powered by advanced SMD (Surface Micro Discharge) cold plasma technology was launched by Hyped About Science GmbH on Kickstarter.
- In April 2025, the Atomic Energy Organization of Iran (AEOI) in collaboration with the Jahrom University of Medical Sciences inaugurated its first cold plasma therapy clinic for treating wounds by utilizing local technology.
- In July 2024, Lam Research Corp., launched Lam Cryo 3.0 which is the third generation of the company's production-proven cryogenic dielectric etch technology, further expanding its leadership in 3D NAND flash memory etching.
Cold Plasma Market Report Segmentation
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the Cold Plasma market.
By Pressure
- Low-Pressure Cold Plasma
- Atmospheric Pressure Cold Plasma
By Application
- Wound Healing
- Blood Coagulation
- Dentistry
- Cancer Treatment
- Other Medical Applications
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa (MEA)

